#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#define GLM_ENABLE_EXPERIMENTAL
#include <iostream>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtx/string_cast.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
#include "cow.h"
#include "ppm_io.h"
void convertNDCtoImage(const glm::vec4 vertexNDC, glm::vec4 vertexView, const uint32_t& imageWidth, const uint32_t& imageHeight, glm::vec3& vertexRaster)
{
vertexRaster.x = ((vertexNDC.x + 1.0f) / 2.0f) * imageWidth;
vertexRaster.y = ((1.0f - vertexNDC.y) * 0.5f) * imageHeight;
vertexRaster.z = -vertexView.z;
}
float min3(const float& a, const float& b, const float& c)
{
return std::min(a, std::min(b, c));
}
float max3(const float& a, const float& b, const float& c)
{
return std::max(a, std::max(b, c));
}
bool edge(const glm::vec3& a, const glm::vec3& b, const glm::vec3& c)
{
return (c.x - a.x) * (b.y - a.y) - (c.y - a.y) * (b.x - a.x) >= 0;
// return 1.0f;
}
glm::mat4 lookAt(glm::vec3 campos, glm::vec3 look, glm::vec3 up)
{
glm::vec3 zaxis = glm::normalize(campos - look);
glm::vec3 xaxis = glm::normalize(glm::cross(up, zaxis));
glm::vec3 yaxis = glm::cross(zaxis, xaxis);
glm::mat4 view = {
{ xaxis.x, yaxis.x, zaxis.x, 0 },
{ xaxis.y, yaxis.y, zaxis.y, 0 },
{ xaxis.z, yaxis.z, zaxis.z, 0 },
{ -glm::dot(xaxis, campos), -glm::dot(yaxis, campos), -glm::dot(zaxis, campos), 1 }
};
return view;
}
glm::mat4 perspective(float fovy, float aspect, float near, float far)
{
glm::mat4 pro_matrix =
{
{ 1/(aspect * std::tan(glm::radians(fovy/2))), 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1 / std::tan(glm::radians(fovy/2)), 0, 0 },
{ 0 , 0, -((far + near) / (far - near)), -1 },
{ 0, 0, -2.0f*((far*near)/(far-near)), 0 }
};
return pro_matrix;
}
const uint32_t imageWidth = 640;
const uint32_t imageHeight = 480;
const uint32_t ntris = 3156;
const float nearClippingPlane = 1;
const float farClippingPLane = 1000;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glm::mat4 worldToCamera = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(20, 10, 20), glm::vec3(0, 5, 0), glm::vec3(0, 1, 0));
float t, b, l, r;
PPM ppmOut;
ppmOut.setBinary(true);
struct rgb
{
uint8_t r, g, b;
};
std::vector <rgb> frameBuffer;
frameBuffer.resize(imageWidth * imageHeight);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < imageWidth * imageHeight; ++i) {
frameBuffer[i].r = 0;
frameBuffer[i].g = 0;
frameBuffer[i].b = 0;
}
float* depthBuffer = new float[imageWidth * imageHeight];
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < imageWidth * imageHeight; ++i) {
depthBuffer[i] = farClippingPLane;
}
auto t_start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < ntris; ++i) {
// 삼각형 만들기 = model coordinate
const glm::vec3& v0 = vertices[nvertices[i * 3]];
const glm::vec3& v1 = vertices[nvertices[i * 3 + 1]];
const glm::vec3& v2 = vertices[nvertices[i * 3 + 2]];
// 모델 행렬 = 로컬 -> 뷰
glm::mat4 modelMatrix(1.0f);
// 글로벌 -> 카메라
glm::mat4 viewMatrix = lookAt(glm::vec3(0, 50, 10), glm::vec3(0, 5, 0), glm::vec3(0, 1, 0));
// 로컬 -> 카메라
glm::mat4 modelViewMatrix = viewMatrix * modelMatrix;
//Camera(view) coordinates
glm::vec4 v0e;
glm::vec4 v1e;
glm::vec4 v2e;
//Code here (calculate v0e, v1e, v2e here)
v0e = modelViewMatrix * glm::vec4(v0, 1.0f);
v1e = modelViewMatrix * glm::vec4(v1, 1.0f);
v2e = modelViewMatrix * glm::vec4(v2, 1.0f);
// std::cout << glm::to_string(v0e) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v1e) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v2e) << "\n\n";
glm::mat4 projection = perspective((45.0f), imageWidth / (float)imageHeight, nearClippingPlane, farClippingPLane);
//Clip coodinates
glm::vec4 v0c, v1c, v2c;
// clip = projection * view
//Code here (calculate v0c, v1c, v2c here)
v0c = projection * v0e;
v1c = projection * v1e;
v2c = projection * v2e;
// std::cout << glm::to_string(v0c) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v1c) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v2c) << "\n\n";
//Perspective division (divide v0c.x, v0c.y, v0c.z by v0c.w (same to v1c, v2c)
glm::vec4 v0p = v0c;
glm::vec4 v1p = v1c;
glm::vec4 v2p = v2c;
//Code here
// 모든 좌표값음 -1 ~ 1로 바꿈 = NDC
v0p /= v0c.w;
v1p /= v1c.w;
v2p /= v2c.w;
glm::vec3 v0Raster, v1Raster, v2Raster;
convertNDCtoImage(v0p, v0e, imageWidth, imageHeight, v0Raster);
convertNDCtoImage(v1p, v1e, imageWidth, imageHeight, v1Raster);
convertNDCtoImage(v2p, v2e, imageWidth, imageHeight, v2Raster);
// std::cout << glm::to_string(v0Raster) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v1Raster) << "\n" << glm::to_string(v2Raster) << "\n\n";
//bound box
float xmin = min3(v0Raster.x, v1Raster.x, v2Raster.x);
float ymin = min3(v0Raster.y, v1Raster.y, v2Raster.y);
float xmax = max3(v0Raster.x, v1Raster.x, v2Raster.x);
float ymax = max3(v0Raster.y, v1Raster.y, v2Raster.y);
if (xmin > imageWidth - 1 || xmax < 0 || ymin > imageHeight - 1 || ymax < 0) continue;
uint32_t x0 = std::max(int32_t(0), (int32_t)(std::floor(xmin)));
uint32_t x1 = std::min(int32_t(imageWidth) - 1, (int32_t)(std::floor(xmax)));
uint32_t y0 = std::max(int32_t(0), (int32_t)(std::floor(ymin)));
uint32_t y1 = std::min(int32_t(imageHeight) - 1, (int32_t)(std::floor(ymax)));
//calculat the area of triangle (area)
float area = edge(v0Raster, v1Raster, v2Raster);
for (uint32_t y = y0; y <= y1; ++y) {
for (uint32_t x = x0; x <= x1; ++x) {
glm::vec3 pixelSample(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, 0);
//calculate the areas of three suvdivided triangles
bool w0 = edge(v1Raster, v2Raster, pixelSample); //w0
bool w1 = edge(v2Raster, v0Raster, pixelSample); //w1
bool w2 = edge(v0Raster, v1Raster, pixelSample); //w2
if (w0 >= 0 && w1 >= 0 && w2 >= 0) { //inside
//calculate the ratio here
w0 /= area;
w1 /= area;
w2 /= area;
//calculate the z of pixelSample
float z;
//code here
if (z < depthBuffer[y * imageWidth + x]) {
depthBuffer[y * imageWidth + x] = z;
//calculate normal vector from v0e, v1e, v2e
glm::vec3 n;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].r = n.x * 255;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].g = n.y * 255;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].b = n.z * 255;
}
}
// frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].r = 255;
// frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].g = 255;
// frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].b = 255;
} // 안쪽 for loop
}
} // 바깥쪽 for loop
auto t_end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto passedTime = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(t_end - t_start).count();
std::cerr << "Wall passed time: " << passedTime << "ms" << std::endl;
rgb* p = frameBuffer.data();
ppmOut.load(&p[0].r, imageHeight, imageWidth, 255, "P6");
ppmOut.write("../../output.ppm");
delete[] depthBuffer;
return 0;
}에서
for (uint32_t y = y0; y <= y1; ++y) {
for (uint32_t x = x0; x <= x1; ++x) {
안쪽을 구현한다
이때 사용되는 것이 Barycentric 좌표를 사용한다
Barycentric 좌표란 한 점이 각 점에서 얼마나 떨어져 있는가에 대한 이야기를 하는 것이다

예를 들면, P에 대해서 생각할때 P는 어디쪽에 가중치가 더 높을까? 그리고 그것을 어떻게 표현할까? 라는 것이다
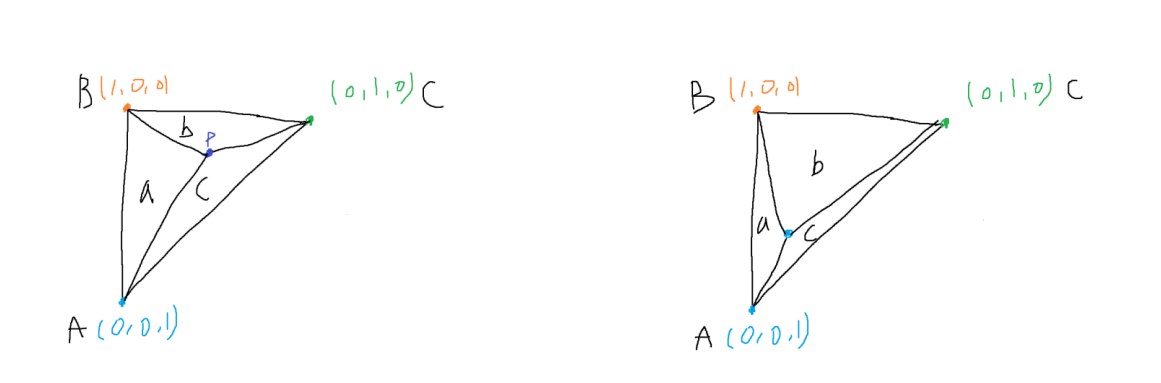
당연히 P가 어디에 있는가에 따라 각 가중치가 달라지게 된다
이때 Barycentric 좌표는 삼각형의 3개 면적을 같게 하는 것을 목표로 하는 한 점 P를 구하는 것이다

이때 삼각형의 전체 면적을 D라고 했을시 해당 수식으로 나타낼 수 있다
// 세개의 꼭짓점으로 이루어진 삼각형 면적
float area(const glm::vec3 a, const glm::vec3 b, const glm::vec3 c)
{
return fabs((c[0] - a[0]) * (b[1] - a[1]) - (c[1] - a[1]) * (b[0] - a[0]));
}이를 코드상에서 구하기 위해 삼각형 면적을 구하는 함수를 작성 후
//calculat the area of triangle (area)
float total = area(v0Raster, v1Raster, v2Raster);
for (uint32_t y = y0; y <= y1; ++y) {
for (uint32_t x = x0; x <= x1; ++x) {
glm::vec3 pixelSample(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, 0);
//calculate the areas of three suvdivided triangles
bool w0 = edge(v1Raster, v2Raster, pixelSample); //w0
bool w1 = edge(v2Raster, v0Raster, pixelSample); //w1
bool w2 = edge(v0Raster, v1Raster, pixelSample); //w2
if (w0 >= true && w1 >= true && w2 >= true) { //inside
float a2 = area(v0Raster, v1Raster, pixelSample);
float a0 = area(v1Raster, v2Raster, pixelSample);
float a1 = area(v2Raster, v0Raster, pixelSample);
//Barycentric 좌표
a0 /= total;
a1 /= total;
a2 /= total;면적으로 나누어서 Barycentric 좌표를 구해준다
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].r = 255;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].g = 0;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].b = 0;임시로 모든 픽셀을 255, 0, 0으로 하여 모든 색을 red로 고정한 후 출력한다

보정이 잘 되서 나오는 것을 임시로 확인할 수 있다
이제 3d모델의 앞뒤를 확인하기 위해서 카메라와 물체와의 거리를 확인해야 한다
즉, 앞에 있는것 = z값이 높은것을 우선시 해서 앞으로 랜더링 해야 한다
if (w0 >= true && w1 >= true && w2 >= true) { //inside
float a2 = area(v0Raster, v1Raster, pixelSample);
float a0 = area(v1Raster, v2Raster, pixelSample);
float a1 = area(v2Raster, v0Raster, pixelSample);
//Barycentric 좌표
a0 /= total;
a1 /= total;
a2 /= total;
float oneOverZ = v0Raster.z * a0 + v1Raster.z * a1 + v2Raster.z * a2;
float z = 1 / oneOverZ; //이 값이 픽셀의 depth
//랜더링 3d모델 카메라 기준 앞인지 뒤인지 확인, 카메라와 가장 가까운지 확인 해야함
if (z < depthBuffer[y * imageWidth + x]) {
depthBuffer[y * imageWidth + x] = z;
//calculate normal vector from v0e, v1e, v2e
glm::vec3 e1 = glm::vec3(v1e - v0e);
glm::vec3 e2 = glm::vec3(v2e - v0e);
glm::vec3 n = glm::normalize(glm::cross(e1, e2)); // 카메라 노멀벡터
// [-1,1] → [0,1]
n = (n + glm::vec3(1, 1, 1)) * 0.5f;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].r = n.x * 255;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].g = n.y * 255;
frameBuffer[y * imageWidth + x].b = n.z * 255;
}
}각 픽셀마다 색 조정을 거치도록 해주면

형광색 소를 볼 수 있다
'공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 구조 - 기억장치(2025 11 17) (0) | 2025.11.17 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 구조 - 기억장치 모듈 설계, 캐시 메모리(2025 11 11) (0) | 2025.11.11 |
| 데이터베이스 - SQL 프로그래밍 (2025 11 10) (0) | 2025.11.10 |
| 컴퓨터 구조 - 기억장치 (2025 11 10) (0) | 2025.11.10 |
| QA - Testing (0) | 2025.11.08 |